Bibliography Background About KRIS
Bacteria in Gulf of Maine Atlantic Salmon DPS Watersheds
Both Pugh (2002) and Arter (2004) note that at several locations the Sheepscot River fails to meet Maine DEP water quality standards for Escherichia coli (E. coli). Elevated bacteria levels occurred at four of six impaired sites (Table 2). The same information can be viewed in spatial form in Figure 1, also from Arter (2004). Patterns of impaired values suggest that some problems are tied to point sources while others are more likely from non-point source pollution (NPS). Once again, Halsted (2002) found relationships between low flow and bacteria counts as she had for temperature and D.O. Dill et al. (2002) point out that, although bacteria such as E. coli do not pose a threat of disease to fish, high bacteria counts are often correlated to nutrient inputs from septic systems or farm animals in proximity to streams, which then have ripple impacts on fish and water quality. E. coli is also a concern in the lower Sheepscot because of potential shellfish harvesting. Area closures are often necessary because of high bacteria counts with "approximately 75% of the estuary shoreline below Wiscasset....classified as prohibited, or closed to shellfish harvesting" (Arter, 2004).
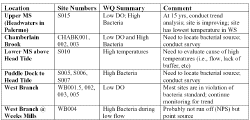 Table 2. This table, from Arter (2004), lists locations of chronic water quality impairment in the Sheepscot River basin and gives water quality summaries and comments regarding needs for additional monitoring.
Table 2. This table, from Arter (2004), lists locations of chronic water quality impairment in the Sheepscot River basin and gives water quality summaries and comments regarding needs for additional monitoring.
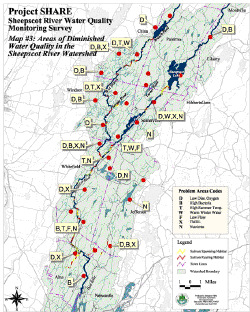 Figure 1. This map from Arter (2004) shows areas of diminished water quality in Sheepscot River. Codes for each site indicate the types of water quality problems that exist and whether the site is listed under the TMDL. Sites with multiple indications of impairment are usually in lower river locations, consistent with Arter's hypothesis that nutrients are accumulating from NPs throughout the watershed. One exception is the reach immediately below Sheepscot Pond, which is affected by the Palermo Hatchery effluent (Arter, 2004).
Figure 1. This map from Arter (2004) shows areas of diminished water quality in Sheepscot River. Codes for each site indicate the types of water quality problems that exist and whether the site is listed under the TMDL. Sites with multiple indications of impairment are usually in lower river locations, consistent with Arter's hypothesis that nutrients are accumulating from NPs throughout the watershed. One exception is the reach immediately below Sheepscot Pond, which is affected by the Palermo Hatchery effluent (Arter, 2004).
References
Arter, B. S., 2004. Sheepscot River Water Quality Monitoring Strategic Plan: A guide for coordinated water quality monitoring efforts in an Atlantic salmon watershed in Maine. Prepared for the Project SHARE: Research and Management Committee. 84 pp. [975kb]
Beland, K., N. Dubé, M. Evers, R. Spencer, S. Thomas, G. Vander Haegen, and E. Baum.1995. Atlantic salmon research addressing issues of concern to the National Marine Fisheries Service and Atlantic Sea Run Salmon Commission. Maine Atlantic Sea Run Salmon Commission Final Project Report NA29FL0131-01.
Chizmas, J. S. 1999. Study of pesticide levels in seven Maine rivers. Maine Board of Pesticides Control. 14 pp [6.2 Mb]
Dill, R., C. Fay, M. Gallagher, D. Kircheis, S. Mierzykowski, M. Whiting, and T. Haines. 2002, Water quality issues as potential limiting factors affecting juvenile Atlantic salmon life stages in Maine rivers. Report to Maine Atlantic Salmon Technical Advisory Committee by the Ad Hoc Committee on Water Quality. Atlantic Salmon Commission. Bangor, ME. 28 pp. [162kb]
Goldman, C.R. and A.J. Horne. 1983. Limnology. McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York . 464 pp.
Halsted, M., 2002. Effects of stream flow on the stream temperature, E. coli concentrations and dissolved oxygen levels in the West Branch of the Sheepscot River. Alna, ME. 15 pp. [450kb]
Haines, T., and J. Akielaszek. 1984. Effects of acidic precipitation on Atlantic salmon rivers in New England. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service FWS/OBS-80/40.18.
Haines, T., S. Norton, J. Kahl, C. Fay, S. Pauwels, and C. Jagoe. 1990. Intensive studies of stream fish populations in Maine. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Acid Deposition, Environmental Monitoring and Quality Assurance, EPA/600/3-90/043.
Kroglund, F., and M. Staurnes. 1999. Water quality requirements of smolting Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) in limed acid rivers. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 56: 2078-2086.
Magee, J. 2001. Agrochemical monitoring and potential effects on Atlantic salmon in eastern Maine rivers. National Marine Fisheries Service Report.
Maine Department of Agriculture. 2002. Report on activities in Atlantic Salmon Conservation Plan Rivers 2002. Maine Dept. of Ag.
Maine Department of Environmental Protection. 2002. Water quality concerns and effects from state fish hatchery discharges. Unpublished Report. Augusta, ME.
Maine Department of Environmental Protection. 2004. 2002 Section 303(d) Report: Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) Waters. Augusta, ME.
National Research Council, 2003. Atlantic Salmon in Maine. The Committee on Atlantic Salmon in Maine, Board on Environmental Studies and Toxicology, Ocean Studies Board, Division on Earth and Life Sciences. National Research Council of the National Academies. National Academy Press. Washington, D.C. 260 pp. [3.5Mb]**
Pugh, L., 2002. Analysis summary of water quality monitoring data, 1994-2001. Sheepscot Valley Conservation Association . Alna, ME. 6 pp. [225kb]
Robinson, K. W., J. P. Campbell, and N. A. Jaworski, 2003. Water quality trends in New England rivers during the 20th century. United States Geologic Service. Water-Resources Investigations Report 03-4012. Pembroke, NH. 29 pp. [950kb]
State of Maine. (1998). Maine Section 303(d) Waters list. http://www.state.me.us/dep/blwq/docmonitoring/303d981.pdf.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 1986. Quality criteria for water 1986: EPA 440/5-86-001. Office of Water Regulations and Standards, Washington D.C.
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, 2000. Endangered and Threatened Species; Final Endangered Status for a Distinct Population Segment of Anadromous Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) in the Gulf of Maine. Federal Register Notice Vol. 65, No. 223 / Friday, November 17, 2000 / Rules and Regulations. Pages 69459-69483 [225kb]
Whiting, M., 2001a. Year 2000 Progress Report for DEP Water Quality Monitoring Plan - Maine Atlantic salmon rivers. Maine DEP, Bangor Regional Office. Bangor, ME. 4 pp. [25kb]
Whiting, M., 2001b. Progress report: A summary of water quality monitoring results from Spring 2001, Maine Atlantic Salmon Rivers Project. Maine DEP, Bangor Regional Office. Bangor, ME. 6 pp. [775kb]**
Whiting, M., 2002. Maine Salmon rivers water quality monitoring progress report for 2002 field season. Maine DEP, Bangor Regional Office. Bangor, ME. 22 pp. [2.25Mb]**
Williams, S. 2002. Maine Volunteer Lake Monitoring Program Annual Report 2002. Maine Volunteer Lake Monitoring Program, Auburn, Maine. 52pp. [7 Mb] http://www.mainevolunteerlakemonitors.org/.
Williams, S. 2003. Maine Volunteer Lake Monitoring Program Annual Report 2002. Maine Volunteer Lake Monitoring Program, Auburn, Maine. 52 pp. [8 Mb] http://www.mainevolunteerlakemonitors.org/.
